There’s a lot of talk about rising levels of carbon dioxide these days. So let’s take a quick look at its deadly cousin.
One of the most prominent factors that no one seems to be talking about in climate change is the incredible increase of carbon monoxide (CO) and decrease of oxygen in Earth’s atmosphere in recent years.
Recent studies have found that our atmosphere has the highest amount of carbon monoxide levels in the last 800,000 years and averaging around 411 Parts per Million (ppm). Three years ago, the average levels were 208 ppm, which equates to a 68% increase in just a mere three years. This increase has been documented in the past, however it would taken over 250 years to change this much.
Before 1990, CO levels increased an average of a 0.5% or less increase per year. Since 1990 the average annual rise is 2% or higher. This means that since 1990 there has been more than a 56% increase in carbon monoxide levels.
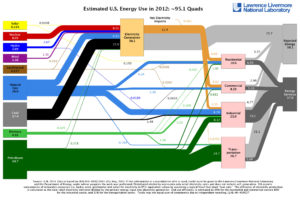
Next time you consider burning, which is pretty much anything, please remember the carbon monoxide it produces. This can be your vehicle, a woodstove fire, or even electricity that is generated by coal, oil, or natural gas.
Alternative products are renewable technologies like wind and solar panel electric as well as hydrogen fuelled catalytic convertors that produce water as a by-product.